In 2026, ecommerce CRO is less about “one big redesign” and more about disciplined conversion rate optimization for ecommerce: speed standards are stricter, mobile expectations are higher, and measurement is messier because consent choices change what you can reliably track. (Yes, that’s annoying. It’s also why a clean CRO process matters more than ever.) The upside: most stores still leak money in the same predictable places—landing pages, product pages, cart, and checkout—so you can boost conversion rates with practical fixes, not vibes. This guide is built like a CRO playbook: prioritize, diagnose, test, and keep what works.
The CRO Priority Stack (Quick Wins → Bigger Bets)
If you want ecommerce CRO to feel “easy,” it’s not because CRO is easy. It’s because your prioritization is ruthless. Here’s the CRO Priority Stack I use when teams ask, “What do we fix first to boost conversion rates?”
Quick Wins (Hours To Days)
- Checkout friction removal: simplify forms, reduce fields, clarify errors. Baymard’s checkout benchmarks show the average U.S. checkout still includes far more form elements than an ideal flow.
- Product page clarity: stronger size/fit info, delivery/returns visible, fewer surprises (the “hidden tax” on trust).
- Speed triage: fix obvious LCP/INP issues (hero image, JS bloat). Core Web Vitals thresholds are clear and public.
- Mobile checkout cleanup: input types, autofill, sticky CTA, fewer taps. This is mobile ecommerce UX 101, yet it’s still broken on many stores.
Medium Lifts (1–3 Weeks)
- Landing page optimization by intent: align message-to-product, remove dead ends, improve internal navigation for category pages.
- Cart abandonment recovery: smarter cart UX + recovery flows (email/SMS) that match the reason users left (not just “come back pls”).
- User behavior analytics setup: consistent events, funnels, and session review routines (so CRO isn’t guesswork).
Bigger Bets (3–8 Weeks)
- Checkout architecture changes: restructure steps, reduce page transitions, improve address validation and payment flow.
- Testing program: real A/B testing for ecommerce with a backlog, guardrails, and a measurement plan.
- Offer and merchandising experiments: bundles, subscriptions, post-purchase upsells, and pricing presentation (done carefully, not randomly).
Editorial aside: If your team is stuck in “we need a redesign,” push back. In CRO, redesign is often a way to avoid making the hard, specific decisions.
Set Your CRO Baseline (So You Don’t Fix The Wrong Thing)
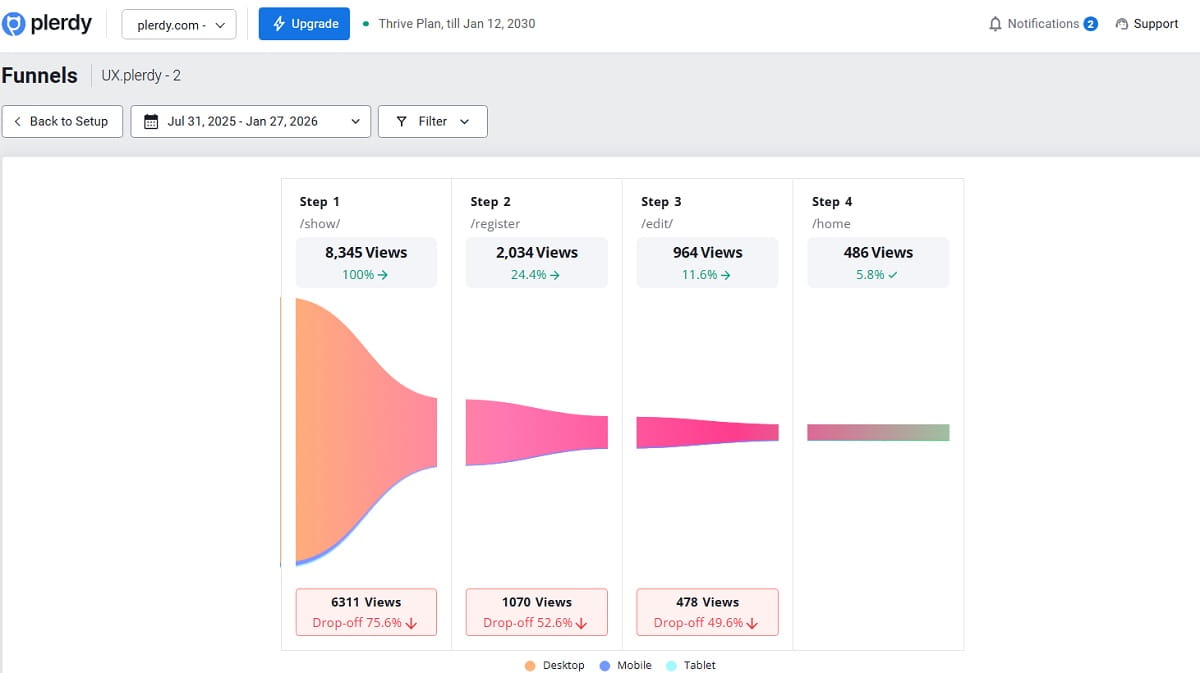
Conversion rate optimization for ecommerce starts with one unsexy truth: if you can’t consistently measure the funnel, your CRO decisions will be political, not factual. In 2026, measurement gets extra tricky because consent choices affect tracking and attribution. Google’s consent mode guidance (including v2 upgrades) is explicit about additional consent parameters and how tags should behave when consent is missing.
Define The Funnel In Events (Before You Touch Design)
For ecommerce conversion rate tracking, your baseline should include at least: product views, add to cart, begin checkout, and purchase. Google documents recommended ecommerce-related events and ecommerce measurement guidance for GA4.
Pick A North Star Metric And Two Guardrails
- North star: ecommerce conversion rate (or completed orders per session) for the segment you’re optimizing.
- Guardrail 1: revenue per visitor (so CRO doesn’t “win” by discounting into the ground).
- Guardrail 2: refund rate / support tickets / delivery issues (because post-purchase pain kills future conversion).
Where Plerdy Fits (Diagnosis → Hypothesis → Test → Verify)
Use Plerdy when you need user behavior analytics that teams can actually act on: heatmaps, scroll maps, and session replay to see where users hesitate and rage-click, plus funnel-style analysis to identify where the journey breaks. Plerdy documents these product areas (heatmaps, session replay, funnels) on its site.
If you want a fast “first pass” before you install anything, Plerdy’s UX & Usability Testing Chrome extension can generate AI-predicted behavior maps and a page review—useful for quick CRO hypotheses (and it’s explicitly described as a prediction, not real user data).
Landing And Category Pages: Make Intent Obvious
Landing page optimization and category page CRO fail for one main reason: the page doesn’t answer the visitor’s “Am I in the right place?” question in the first few seconds. If the intent is unclear, your ecommerce CRO work downstream won’t matter because the wrong people will bounce or wander.
People Also Ask: What Should I Fix First On A Category Page?
Start with clarity and navigation. Category pages should help users self-select quickly: filters that make sense, product cards that reduce uncertainty, and visible shipping/returns context. CRO is often blocked by “invisible confusion”—the page looks fine, but users don’t know what to click next.
High-Impact CRO Moves For Landing And Category Pages
- Match the promise to the page: if the ad says “Waterproof winter boots,” don’t land them on “All shoes.” That kills ecommerce conversion rate quietly.
- Fix “dead ends”: if users click a product card and nothing happens, that’s a direct revenue leak. (You’d be shocked how often this happens after theme edits.)
- Reduce filter fatigue: fewer, smarter filters; clear defaults; keep mobile filter UX simple.
- Product card sanity: show price, key variant info, rating (if real), delivery promise, and returns link nearby.
- Trust without clutter: shipping, returns, and support links should be accessible, not buried in a footer maze.
Mini Example (Generic): The “Too Many Collections” Problem
Example: A store runs paid traffic to a “New Arrivals” category, but the page has 14 competing navigation elements, a banner slider, and filters that collapse into a tiny icon on mobile. User behavior analytics typically shows quick taps, scroll spikes, and back button exits. The CRO fix isn’t “make it prettier”—it’s simplifying the path: one clear filter entry point, a sticky sort, and product cards that answer basic questions without extra taps.
Do This Today: Landing And Category CRO Checklist
- Open your top 3 landing pages on mobile and ask: “What do I do next?” If it’s not obvious, CRO is already losing.
- Check for dead clicks on product cards, images, and filter controls using heatmaps and session recordings.
- Verify category filters are usable with one thumb (mobile ecommerce UX is not optional).
- Confirm page speed basics: large hero images, heavy scripts, and layout shifts (CLS) are common CRO killers.
Product Page Optimization: Remove “Silent No’s”
Product page optimization is where ecommerce CRO makes or breaks the sale. Most product pages don’t fail because the product is bad. They fail because the page creates uncertainty: sizing, delivery, returns, authenticity, compatibility, or “what happens after I click buy?”
People Also Ask: What Are The Biggest Product Page CRO Mistakes?
The biggest CRO mistakes are uncertainty and friction: unclear variant selection, hidden shipping costs/timelines, weak size guidance, confusing imagery hierarchy, and add-to-cart buttons that compete with distractions. A clean product page is not “minimal.” It’s decisive.
Product Page CRO That Actually Moves The Needle
- Make variants impossible to mess up: label sizes clearly, show availability, and explain fit.
- Put delivery and returns near the CTA: don’t make users hunt. It’s conversion rate optimization for ecommerce, not a scavenger hunt.
- Use images as answers: show the product in context, show scale, show details that reduce objections.
- Stop hiding the total cost story: shipping, taxes, and delivery time are trust signals; surprise costs spike cart abandonment.
- Use urgency carefully: fake countdown timers often reduce trust. CRO is not “tricks.”
How To Use Heatmaps And Session Recordings On Product Pages
Heatmaps and session recordings are useful because they show where product page UX breaks: repeated taps on non-clickable elements, rage clicks on size charts, scroll depth drop-offs before the reviews, and confusion around the add-to-cart area. Plerdy’s heatmap and session replay tools are designed for these workflows.
Mini Example (Generic): The Size Chart Trap
Example: A fashion store sees high product views but low add-to-cart. In session recordings, users open the size chart, pinch-zoom, then exit. In a CRO audit, the fix is straightforward: replace the image-based chart with a readable, mobile-first chart; add “How to measure” microcopy; and show fit notes above the fold. This is product page optimization that reduces uncertainty, which boosts conversion rates without changing the offer.
Do This Today: Product Page CRO Checklist
- Move shipping and returns info within one scroll of the CTA.
- Audit variant selection on mobile (one-thumb, no tiny tap targets).
- Watch 10 session recordings from mobile product pages; list the top 3 hesitation points.
- Use scroll depth to confirm users reach key trust sections (reviews, materials, warranty).
Cart: Reduce Cart Abandonment Before Checkout Even Starts
Cart abandonment is not just a checkout issue. The cart itself often creates friction: surprise costs, confusing discount logic, forced cross-sells, or unclear delivery details. Ecommerce CRO here is about making the cart feel like a confident summary, not a warning label.
Cart UX That Supports Conversion Rate Optimization For Ecommerce
- Show the real total cost story: estimate shipping if you can, clarify taxes, and avoid surprises.
- Make “edit cart” easy: quantity changes, remove, save for later—without reload lag or weird UI jumps.
- Discount code UX: don’t make it a trap. If you show a promo field, users will go hunting for codes and abandon. Consider hiding it behind a link (“Have a code?”) if appropriate.
- Progress cues: show what’s next and how long it takes. CRO loves clarity.
Do This Today: Cart CRO Checklist
- Check the cart on mobile: can you update quantity without zooming?
- Confirm cart loads fast and doesn’t jump around (CLS).
- Review session recordings for “coupon hunting” behavior and confusing price changes.
Checkout Optimization: Fewer Frictions, Fewer Form Elements
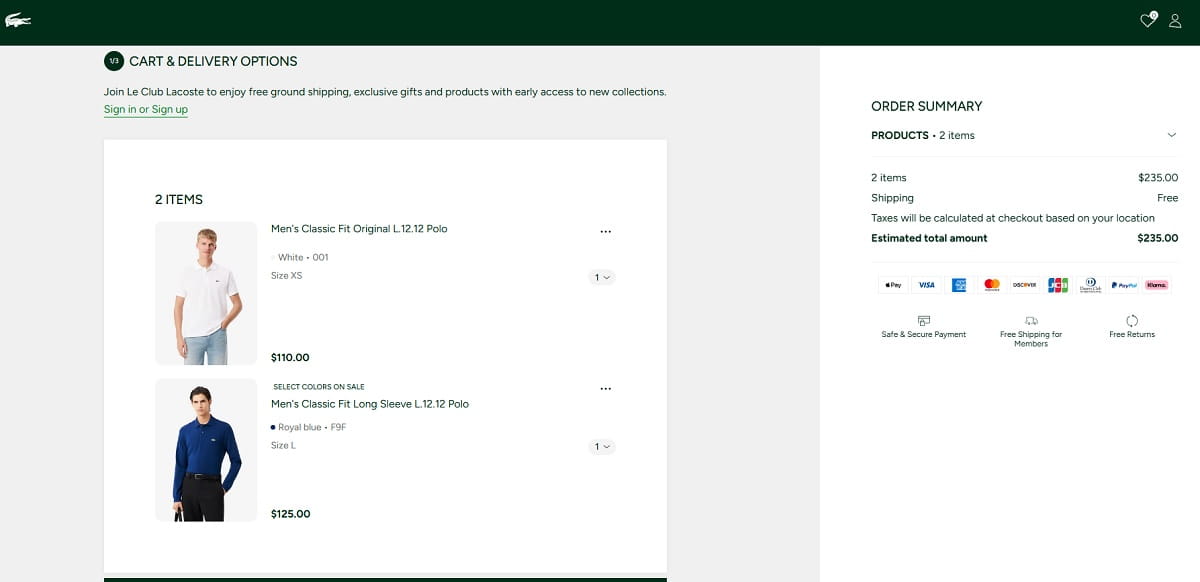
Checkout optimization is the highest-leverage ecommerce CRO lever because users are already motivated. The problem is that many checkouts still feel like paperwork. Baymard’s research and benchmarks repeatedly highlight friction points like complex flows and excessive form elements; their published checkout benchmarks include an average U.S. checkout flow with 23.48 form elements displayed by default.
People Also Ask: How Many Fields Should Checkout Have?
There isn’t a single universal number, but Baymard’s large-scale checkout testing suggests an ideal checkout flow can be significantly shorter than what many retailers currently show, and their benchmarks highlight how far typical checkouts drift into complexity.
Checkout Optimization Moves That Usually Improve Ecommerce Conversion Rate
- Guest checkout by default: account creation is a classic friction point. Offer account creation after purchase.
- Make errors gentle: inline validation, clear error messages, preserve user input. Nothing kills CRO faster than “form rage.”
- Use the right input types on mobile: numeric keypad for phone/postal, autofill-friendly fields.
- Reduce address pain: auto-complete where possible, clear country/state logic, avoid forcing formats.
- Don’t hide delivery cost/timing: unclear shipping is cart abandonment fuel.
- Payment clarity: show available payment methods early; confirm total cost before final action.
Consent And Tracking Reality In 2026 (Don’t Break Measurement During Checkout Changes)
Checkout CRO can accidentally break tracking: form restructuring, URL changes, or tag firing changes can drop events. If you operate in the EEA or serve EEA traffic, Google’s consent mode documentation (including v2 upgrades) outlines required consent parameters beyond ad_storage and analytics_storage (like ad_user_data and ad_personalization) and how measurement use cases depend on them.
Practical CRO takeaway: before you ship checkout optimization changes, verify your begin_checkout and purchase events still fire as expected (GA4 ecommerce measurement guidance is documented).
Do This Today: Checkout CRO Checklist
- Count how many form elements your checkout shows by default; compare against Baymard’s benchmark context and ask what can be removed.
- Run a mobile checkout pass with one hand. Any “two-hand moments” are CRO friction.
- Test errors intentionally (wrong card, missing zip, invalid phone) and see if the flow recovers gracefully.
- Confirm GA4 ecommerce events still fire after any checkout changes.
Post-Purchase CRO: Retention, Upsells, Fewer Refunds
Post-purchase is often ignored in ecommerce conversion rate optimization, but it matters because it affects repeat purchase, referrals, and refunds—plus it influences what users say in reviews (which affects future CRO). Post-purchase CRO isn’t “spam upsells.” It’s making customers feel safe about their decision.
Post-Purchase CRO That Pays Off
- Order confirmation clarity: what happens next, delivery timeline, tracking, and support contact.
- Reduce buyer’s remorse: reinforce key benefits and correct usage (especially for products with setup).
- Upsells with relevance: accessories that genuinely fit the product (not random “people also bought”).
- Prevent refunds: proactive FAQs, sizing guidance follow-up, and easy exchange flows.
Where Plerdy Helps Post-Purchase CRO
If customers keep contacting support about the same confusion (“Where’s tracking?” “How do I use it?”), you can use session replay and funnels to see where users get lost in the post-purchase journey. Plerdy’s session replay and funnel analysis positioning is documented on its site.
Do This Today: Post-Purchase CRO Checklist
- Read your last 50 support tickets and label the top 5 confusion themes (that’s your post-purchase CRO backlog).
- Make order tracking and returns policy reachable from the confirmation page within one tap on mobile.
- Add one short “How to get the best result” section for products that cause setup questions.
Mobile Ecommerce UX And Speed: Core Web Vitals And Reality
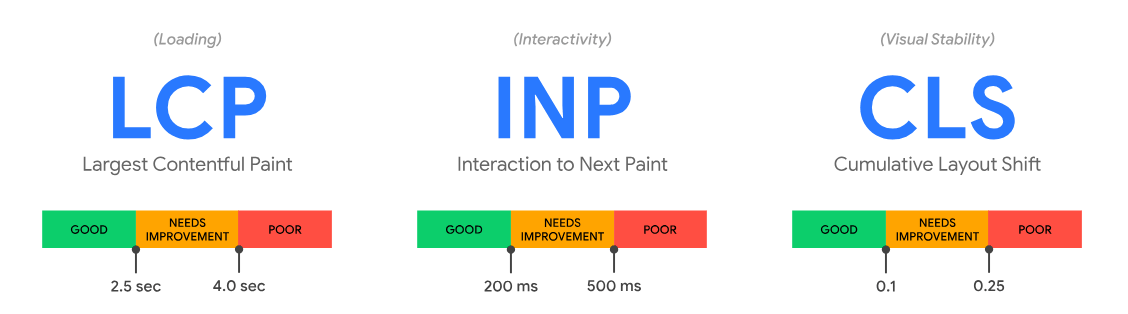
Mobile ecommerce UX and speed are no longer “nice to have.” They are core ecommerce CRO levers. Google’s Core Web Vitals documentation sets clear thresholds for LCP, INP, and CLS (and emphasizes measuring at the 75th percentile in the field).
Core Web Vitals That Matter For CRO (And The 2026 Baseline)
- LCP: aim for 2.5 seconds or less for a good experience (measured at the 75th percentile).
- INP: aim for 200ms or less; INP replaced FID as a Core Web Vital in March 2024.
- CLS: aim for 0.1 or less to avoid layout shifts (the “page jumps while I’m trying to tap” problem).
Google’s Search documentation explains Core Web Vitals as part of page experience considerations and recommends achieving good CWV for success in Search (and, practically, for user satisfaction).
Speed And Conversion: Don’t Argue With Physics
Speed isn’t just SEO; it’s CRO. Google’s Think with Google has published mobile speed and conversion guidance noting that delays can reduce conversion performance.
What Usually Breaks Mobile Ecommerce UX
- Tap targets too small: users miss, then rage-tap (your heatmaps will show it).
- Sticky elements fighting each other: chat widgets, sticky headers, sticky CTAs—stacked into chaos.
- Heavy scripts: popups, trackers, and visual effects can crush INP by blocking the main thread. INP guidance explains how poor responsiveness happens when long tasks block interactions.
- Layout shift surprises: banners load late, reviews widgets pop in, buttons jump (CLS pain).
Do This Today: Mobile And Speed CRO Checklist
- Run PageSpeed Insights on your top 5 landing pages and product pages; check field data focus (75th percentile) and CWV classification.
- Open product page on mobile: can you select variant, add to cart, and reach checkout in under 30 seconds without friction?
- Kill the biggest LCP offender first (often the hero image or a large product image). LCP thresholds and guidance are documented.
- Watch for interaction lag (INP): if taps feel delayed, audit heavy JS and third-party scripts.
A/B Testing For Ecommerce: Experiment Hygiene In 2026
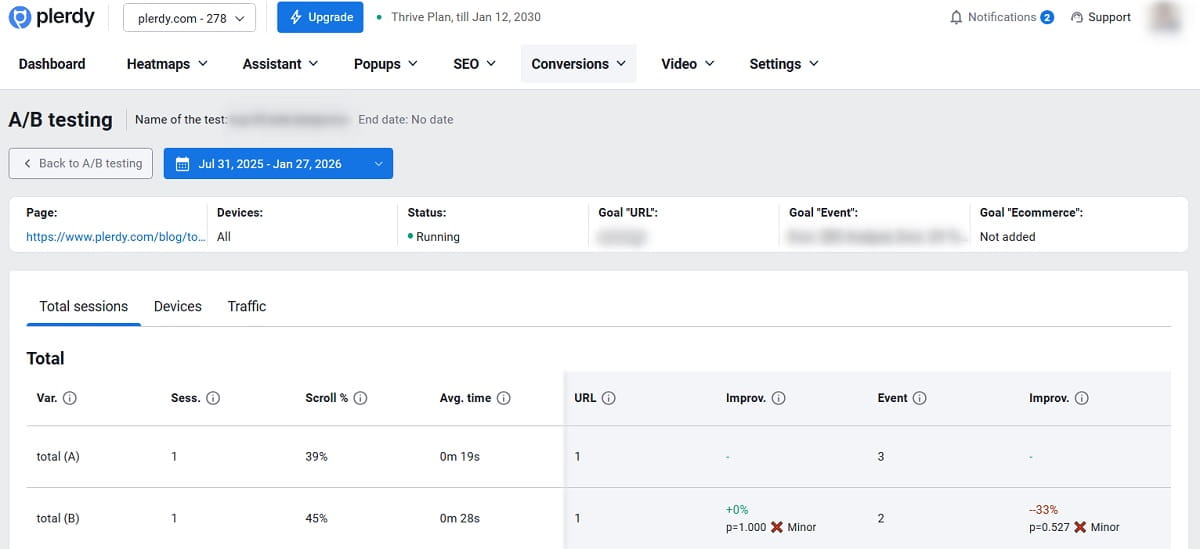
A/B testing for ecommerce is where CRO teams either become trusted—or become “those people who break the site.” The difference is hygiene: clear hypotheses, consistent measurement, and resisting the urge to declare winners too early.
People Also Ask: How Do I Avoid False Winners In CRO Tests?
Use one primary metric, define guardrails, avoid peeking daily, and run tests long enough to cover typical traffic patterns. Sample size estimation depends on your baseline and expected lift; Optimizely’s guidance emphasizes tailoring sample size to the test and metric rather than using one generic rule.
Experiment Design Rules That Keep CRO Honest
- One clear hypothesis: “If we reduce checkout form friction, we will increase purchase completion.” Not “let’s try a new vibe.”
- One primary outcome: ecommerce conversion rate (or purchase completion) for the target segment.
- Guardrails: revenue per visitor, refunds, AOV, support contacts.
- Segment carefully: mobile vs desktop, new vs returning, traffic sources. CRO wins in one segment can lose in another.
- Track implementation: make sure events still fire. GA4 ecommerce event guidance is documented.
How Plerdy Supports A/B Testing Workflows
Good CRO uses qualitative proof (what users do) and quantitative proof (what the funnel shows). Session replay, heatmaps, and funnels help you build better hypotheses and verify whether a “win” actually improved user behavior, not just a metric artifact. Plerdy describes these tool areas publicly.
Do This Today: A/B Testing CRO Checklist
- Write 5 CRO hypotheses from real user behavior (recordings/heatmaps), not brainstorming.
- Choose one primary metric and two guardrails for each test.
- Plan sample size and duration based on your baseline; avoid guessing.
Troubleshooting: If You Change X And Conversions Drop…
This section exists because CRO changes can backfire, and “we’ll just revert” is not always clean (especially with checkout and tracking). Here’s a practical troubleshooting flow for ecommerce CRO teams.
If You Simplify Checkout And Purchases Drop
- Check tracking first: did begin_checkout or purchase events break? Use GA4 ecommerce guidance to validate event structure.
- Look for payment method issues: did you hide a preferred method or change its visibility?
- Audit validation: did you introduce a confusing error state or wipe user input?
- Review session recordings: are users stuck, retrying, or bouncing on a specific step?
If You Improve Speed And Conversion Doesn’t Move
- Confirm you improved field CWV, not just lab scores: PageSpeed Insights explains field metric reporting at the 75th percentile.
- Check intent and offer clarity: CRO is not only speed; speed is an enabler.
- Look at mobile UX friction: speed without usability still loses conversions.
If You Change Product Page Layout And Add-To-Cart Drops
- Find hesitation spots: heatmaps and scroll depth often show users missing critical info after a layout change.
- Check variant selection: did you make size/color selection less obvious on mobile?
- Verify CTA visibility: is the CTA pushed below the fold on common devices?
Run A CRO Audit: A Practical Checklist
A CRO audit is not a spreadsheet of “best practices.” A CRO audit is a structured walk through your funnel with evidence: analytics, user behavior analytics, and real sessions. In 2026, you need a CRO audit rhythm, not a one-time event.
CRO Audit Step 1: Map The Funnel And Drop-Off Points
- Define the funnel: landing → product → cart → begin checkout → purchase.
- Identify the biggest drop-offs (and segment by mobile vs desktop).
- Flag “high traffic, low conversion” pages for CRO attention.
CRO Audit Step 2: Diagnose With User Behavior Analytics
- Review heatmaps for dead clicks, missed CTAs, and confusing UI hotspots.
- Watch session recordings for the top drop-off steps (you want patterns, not one-off stories).
- Use funnel analysis to confirm where users exit the journey.
CRO Audit Step 3: Check Core Web Vitals On Money Pages
- Validate LCP, INP, and CLS on product and checkout pages.
- Remember: INP replaced FID in March 2024; responsiveness matters for perceived quality.
- Use field data where possible; PSI explains 75th percentile reporting.
CRO Audit Step 4: Prioritize And Ship
- Pick 3 quick wins, 2 medium lifts, 1 bigger bet (use the CRO Priority Stack above).
- Write hypotheses and decide measurement guardrails.
- Ship changes in controlled batches so you can attribute outcomes.
The 7 Actions That Move Ecommerce Conversion Rate Most
If you want a clean summary, here’s the “do this, not that” list for ecommerce CRO in 2026. This is conversion rate optimization for ecommerce that respects reality: speed, mobile, checkout friction, and measurement constraints.
- Start with checkout optimization and remove obvious friction (form elements, errors, guest checkout). Use Baymard benchmarks as a reality check.
- Fix product page uncertainty (variants, shipping/returns, trust info near the CTA). Product page optimization is where intent becomes purchase.
- Make category pages decisive (filters, navigation, product card clarity). Landing page optimization is often “make it obvious.”
- Get mobile ecommerce UX right (tap targets, sticky CTA sanity, fewer taps, better inputs).
- Hit Core Web Vitals thresholds on money pages (LCP/INP/CLS) and focus on field experience at the 75th percentile.
- Build CRO around evidence using user behavior analytics (heatmaps and session recordings) to generate and validate hypotheses.
- Run A/B testing for ecommerce with hygiene (clear hypotheses, guardrails, sample size planning).
If you do those seven things consistently, you’ll boost conversion rates in a way that’s repeatable—not dependent on luck, trends, or one “viral” redesign. That’s what good CRO looks like.
FAQPage Markup For WordPress (HTML Only, No JSON)
What Is Ecommerce CRO In 2026?
Ecommerce CRO is conversion rate optimization for ecommerce: improving the shopping experience and funnel so more visitors complete a purchase. In 2026, CRO also means meeting Core Web Vitals expectations and dealing with measurement complexity when consent choices limit tracking.
Where Should I Start If I Want To Boost Conversion Rates Fast?
Start with checkout optimization and product page optimization. Checkout friction and product-page uncertainty are common, high-impact reasons ecommerce conversion rate stays low. Fix those first, then move up-funnel to landing and category pages.
How Do Core Web Vitals Affect Ecommerce Conversion Rate?
Core Web Vitals reflect real-user experience for loading (LCP), responsiveness (INP), and stability (CLS). Poor scores create friction and frustration—especially on mobile—which hurts ecommerce CRO and can reduce conversion performance.
What Changed With INP And Why Should CRO Teams Care?
INP replaced FID as a Core Web Vital in March 2024. It focuses on interaction responsiveness, so delayed taps, slow dropdowns, and heavy scripts can directly increase drop-offs in product pages, cart, and checkout.
How Do I Reduce Cart Abandonment Without Guessing?
Use funnels to locate drop-offs, then review heatmaps and session recordings to identify friction patterns like confusing totals, coupon hunting, and broken UI. Fix the biggest patterns first and validate outcomes with structured testing.
How Should I Set Up Measurement For Ecommerce CRO In 2026?
Track consistent ecommerce events (view_item, add_to_cart, begin_checkout, purchase) and re-verify them after UX changes. If you serve EEA traffic, align tagging with consent requirements so measurement doesn’t silently degrade when consent is denied.
How Do I Avoid Bad A/B Tests In Ecommerce CRO?
Define one hypothesis, one primary metric, and clear guardrails. Plan sample size from your baseline, avoid early “winner” calls, and segment carefully (mobile vs desktop, new vs returning) so you don’t ship false winners.
Where Does Plerdy Fit Into An Ecommerce CRO Workflow?
Plerdy fits best in diagnosis and validation: heatmaps and scroll depth show interaction patterns, session recordings reveal friction and hesitation, and funnels pinpoint drop-offs. The Chrome extension can generate AI-predicted behavior maps for fast hypothesis generation.
